2025 Author: Jasmine Walkman | [email protected]. Last modified: 2025-01-23 10:18
The cassava shrub is native to South America and is distributed in the tropics and Thailand. It is used to make the popular tapioca, which feeds 1/3 of Africa.
Cassava is a plant that requires minimal care for rich harvests. Starch, extremely rich in calories, is extracted from the tubers and roots. The roots of sweet species are also edible. The plant is second in productivity after sugar cane. Unlike it, however, cassava is suitable for direct consumption and can be processed into flour. The fact that it is among the most productive plants grown for human consumption makes it an alternative food for the future.
The usable parts of cassava are almost all, each of which is loaded with different content. Edible root tubers are rich in starch, and raw roots - a glycoside of the hydrocyanic acid linamarin, manichotoxin. Their concentration divides the varieties into bitter and sweet. Bitter rhizomes are not consumed because doses of hydrocyanic acid are lethal to humans.
In direct consumption, it should be borne in mind that a dose of hydrocyanic acid in only 400 g of raw bitter cassava can be fatal. The consequences range from mild poisoning to ataxia and amblyopia.
Incurable forms of paralysis occur in children. At room temperature, hydrocyanic acid evaporates rapidly. However, its complete neutralization requires careful grinding of the tuber.
The seeds are also eaten. They have a laxative effect and treat nausea and vomiting.
In addition to its culinary application, cassava is useful in other aspects. For example, due to its antiseptic action, it is commonly used in Brazil for canning meat. Cassava ointment is useful for conjunctivitis and corneal ulcers. It is also used in some cosmetic products.
Recommended:
Artificial Foods - Foods Of The Future?

The first artificial burger was presented and eaten at a demonstration in London. The meatball is made from artificial meat, composed of laboratory-grown stem cells. The project leader, physiologist Mark Post, said that in order to give the synthetic meat a normal look, it was colored with food coloring.
They Discovered The Food Of The Future

Many scientists, biologists, geneticists, thinkers and philosophers are wondering how to deal with the growing problem of world hunger. Due to the depletion of resources and the change and change of meteorological conditions, the world powers began attempts to cultivate food and many types of production, which led only to the further destruction of the ecosystem and the creation of harmful GMO foods .
Meat In A Test Tube - The Food Of The Future
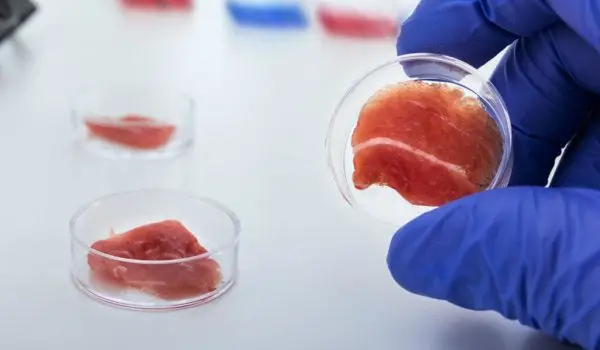
Scientists predict that by 2050 there will be 9.6 billion people on earth and most likely food shortages. That's why they set out to find an alternative to our current food. Powdered food, jellyfish dishes, insects, algae, laboratory meat, faecal water, food patch - these are just some of the options.
Jellyfish Are The Food Of The Future! That's Why

Jellyfish can be the food that will save humanity from starvation in the near future. Their number has been growing so much lately that it offers people an unusual solution to the food problem. Jellyfish in the Mediterranean have reached particularly high levels.
Food In The Cities Of The Future! See What We Will Eat

The future is already here. Some of the world's largest cities are already inventing new ways to feed their fast-growing populations. Laboratory-made steaks and burgers made from plant-based meat will soon tempt sworn carnivores. Demand for meat and dairy products will soon bring to the fore high-protein alternatives that do not seriously pollute the environment.

